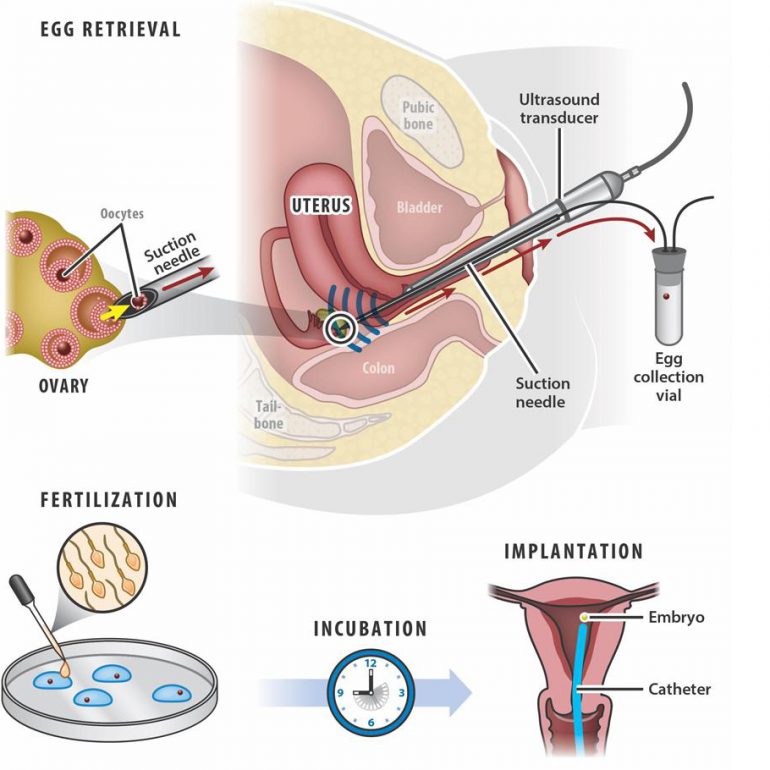
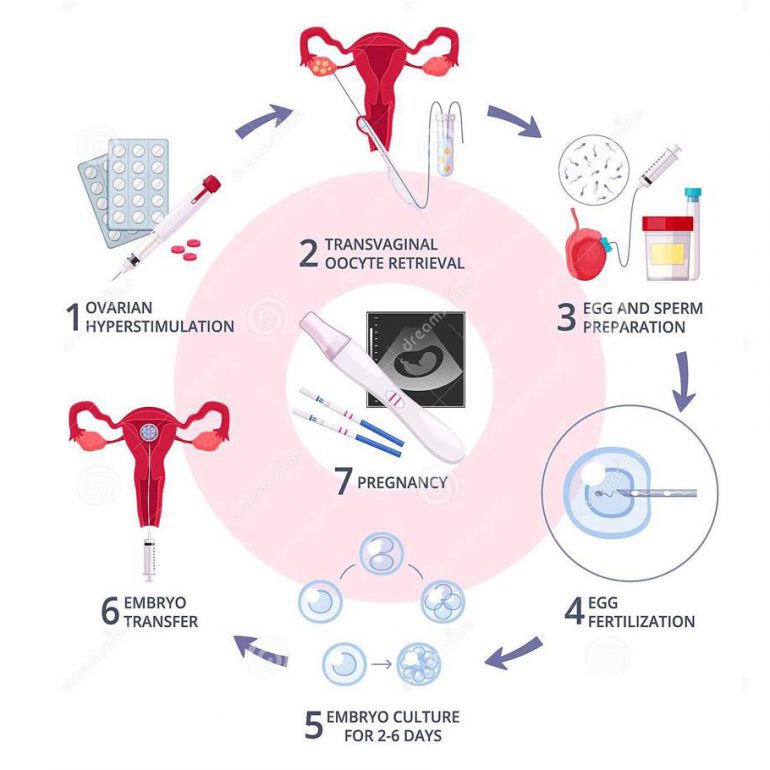
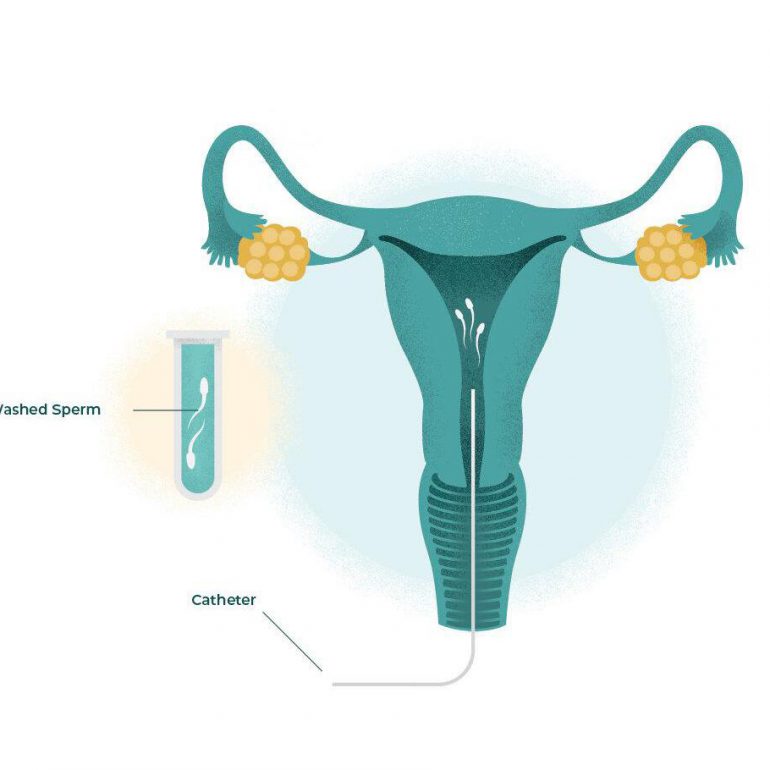
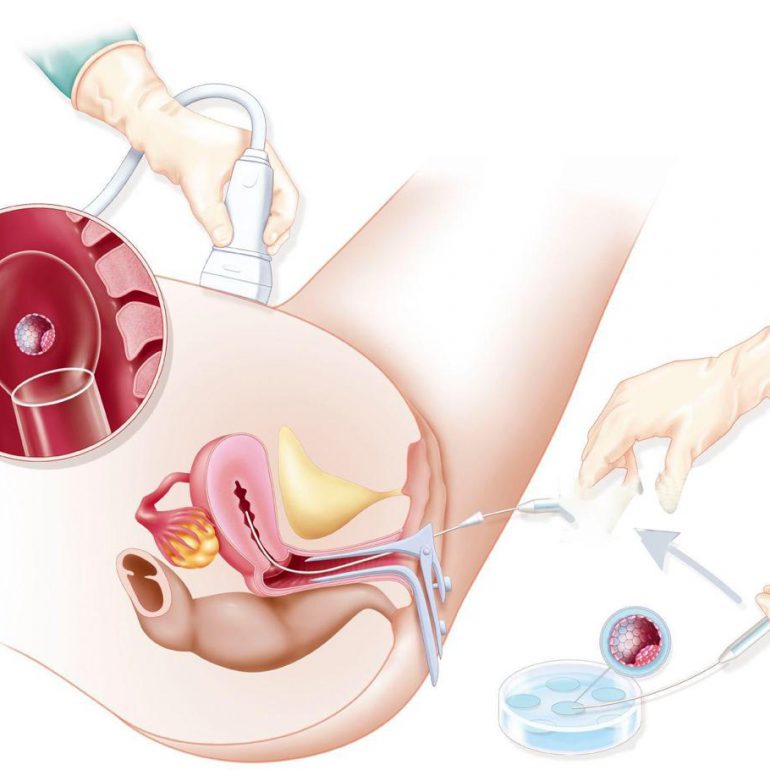
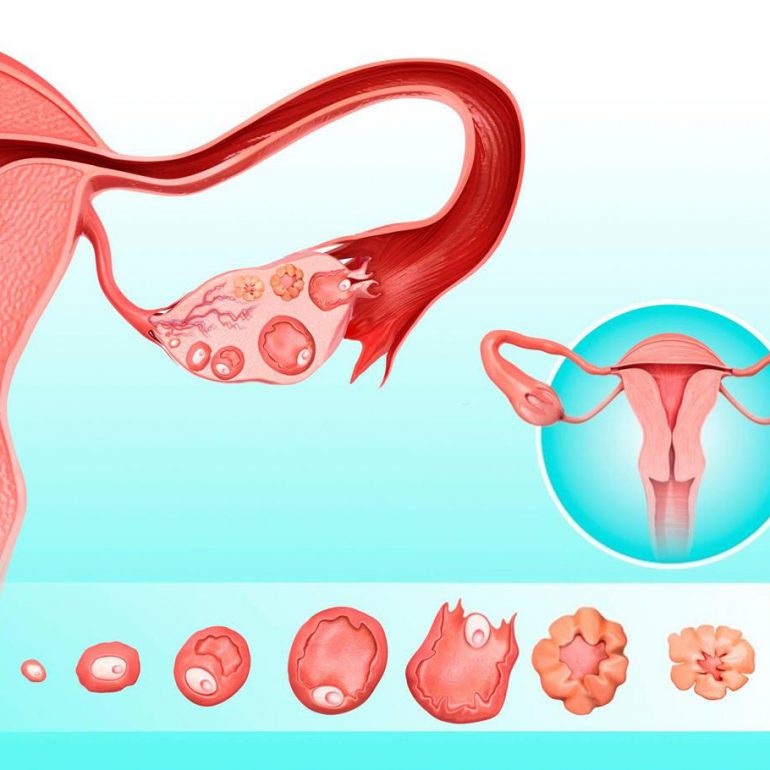
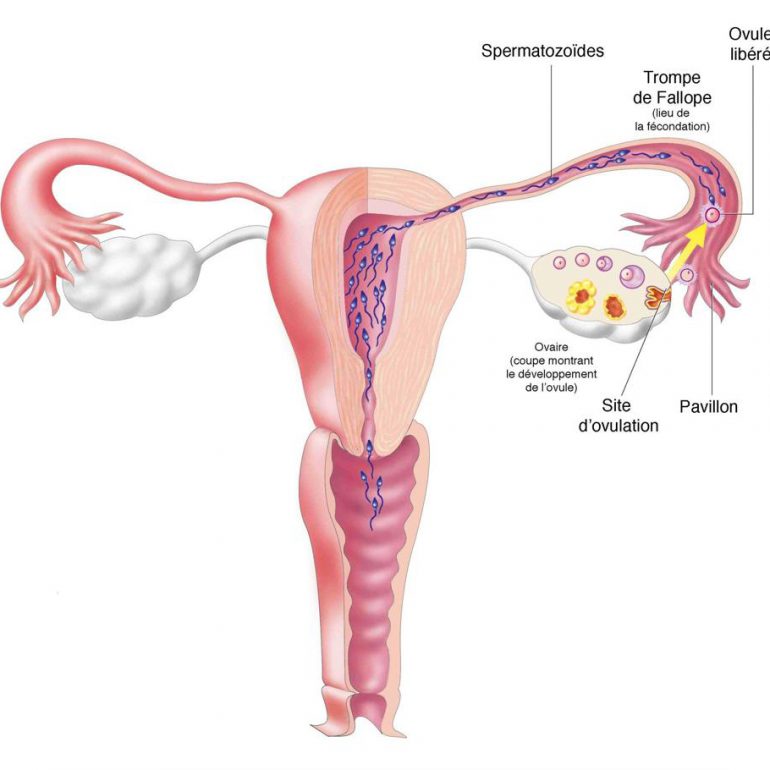
Steps In Vitro
Egg Fertilization
In cases of normal sperm function, the eggs and several thousand sperm are placed together in a dish which contains a culture media. These dishes are kept in an incubator overnight and are examined under the microscope on the morning after the egg retrieval to determine which eggs have fertilized normally. An alternative method of achieving egg fertilization is called Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection, or ICSI. An extremely sharp glass needle is used to inject one sperm directly into the center (cytoplasm) of the egg under the guidance of a specially fitted microscope.
Traditionally, the majority of embryo transfers are performed after 3 days of culture when the embryos have four to eight cells. A concern with this is that Day 3 embryos normally are found in the fallopian tubes, not in the uterus. The embryo first moves into the uterus at about 78-82 hours after ovulation. The implantation process begins about 3 days later, after blastocyst formation and hatching have occurred. Many of the embryos on culture day three do not have the biologic potential to develop into high quality blastocysts (Day 5 embryos). Therefore, the trend has been to transfer more embryos on day 3 in an attempt to achieve acceptable pregnancy rates. By choosing the optimal blastocysts for transfer on day 5, we can select the embryos with the highest potential for implanting and making a baby.