Finney Hospoital & Fertility Center
Fertility Treatment Options
- Ovulation Induction
- ICSI
- IUI
- IVF
Ovulation Induction
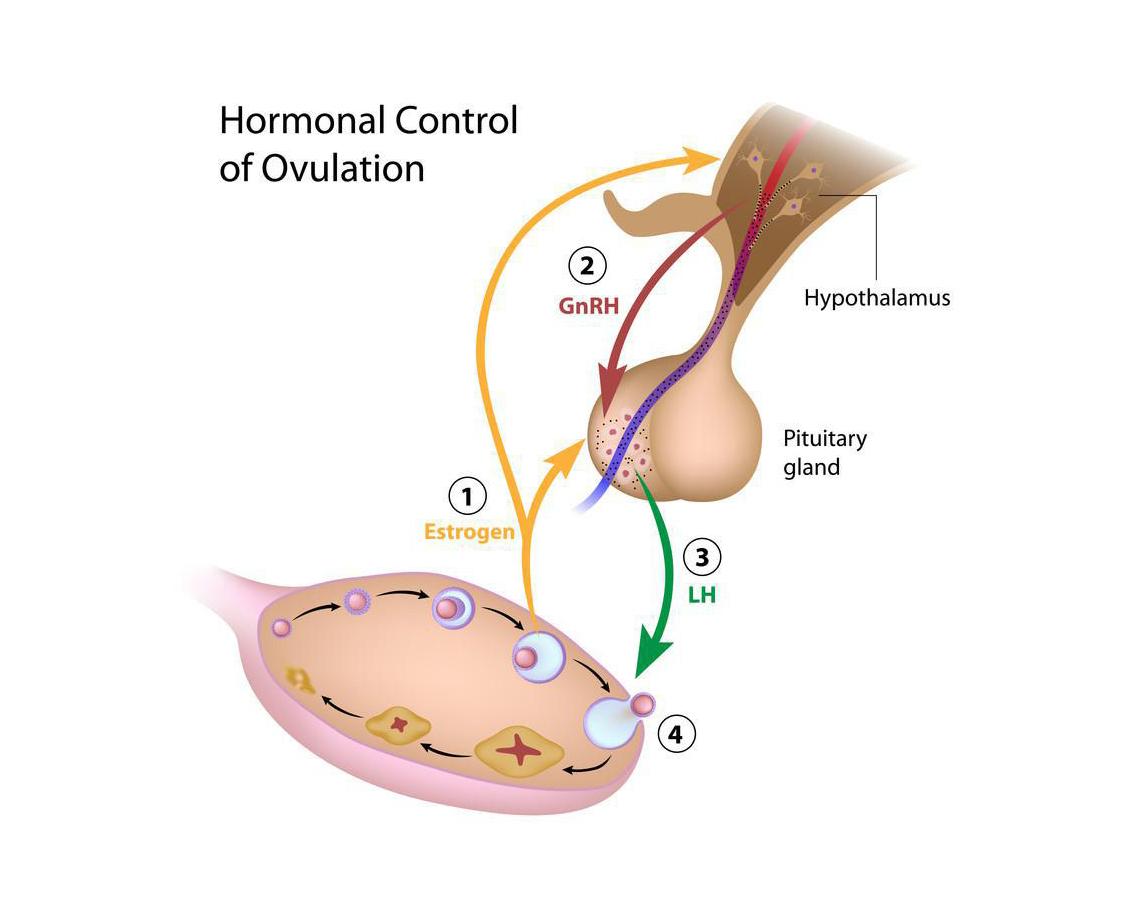
Anovulation is the commonest cause of infertility and the easiest to treat. The treatment is call ovulation induction and the aim is to restore ovulation in the most natural way possible.
It involves the woman taking fertility drugs, either in the form of tablets or injections, to help the ovary produce and release a single egg each month. Injections are only used if there is no response to the milder tablet drugs. The response to the medication is monitored with a series of ultrasound scans in the first half of the cycle (follicle tracking) and a hormone blood test for progesterone 7 days after ovulation
ICSI
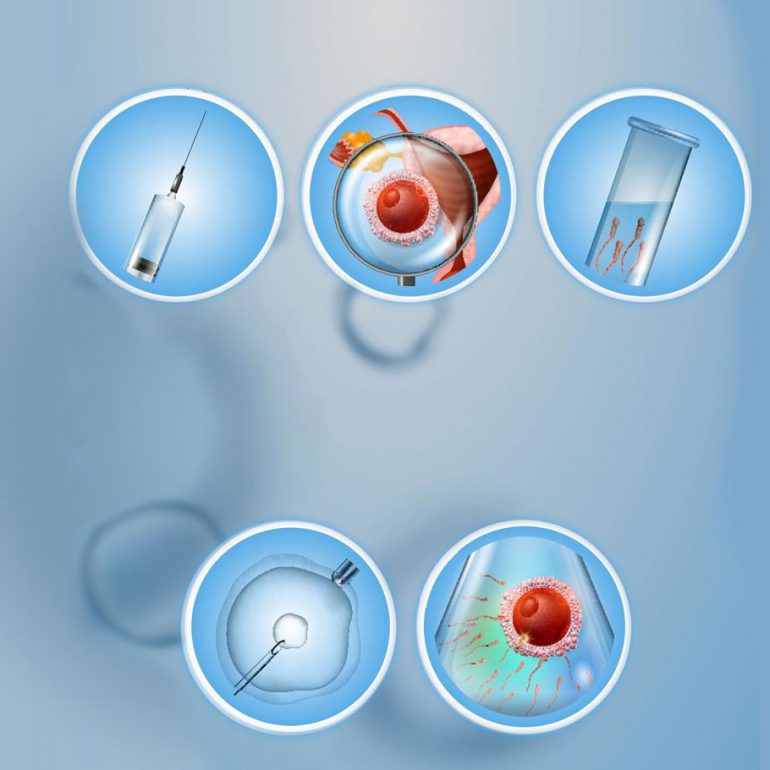
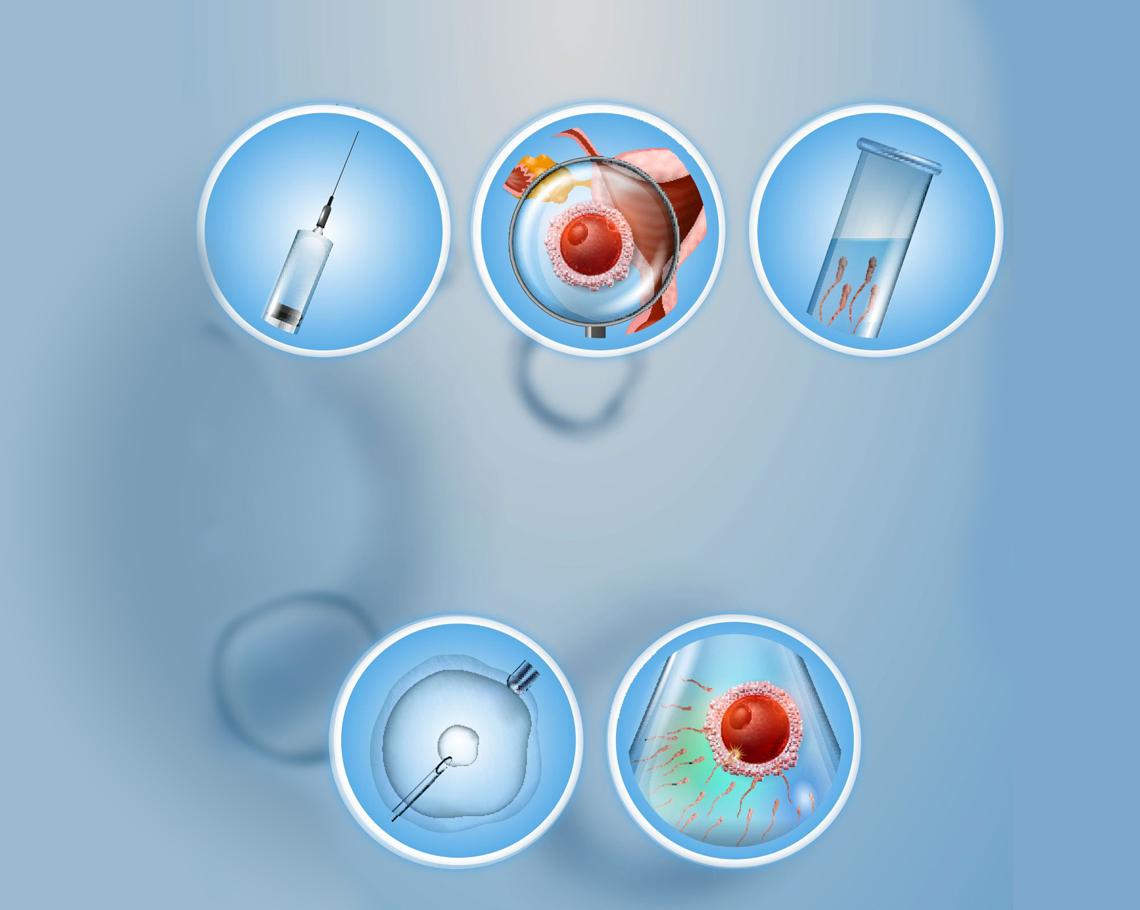
- Intracytoplasmic injection (ICSI) is a special form of IVF in which individual sperm are injected into the egg under microscopic vision.
- This is the treatment advised for couples where the sperm quantity or quality is very poor or when IVF has resulted in failed fertilisation. It is also used when the sperm has been collected through surgical sperm retrieval...

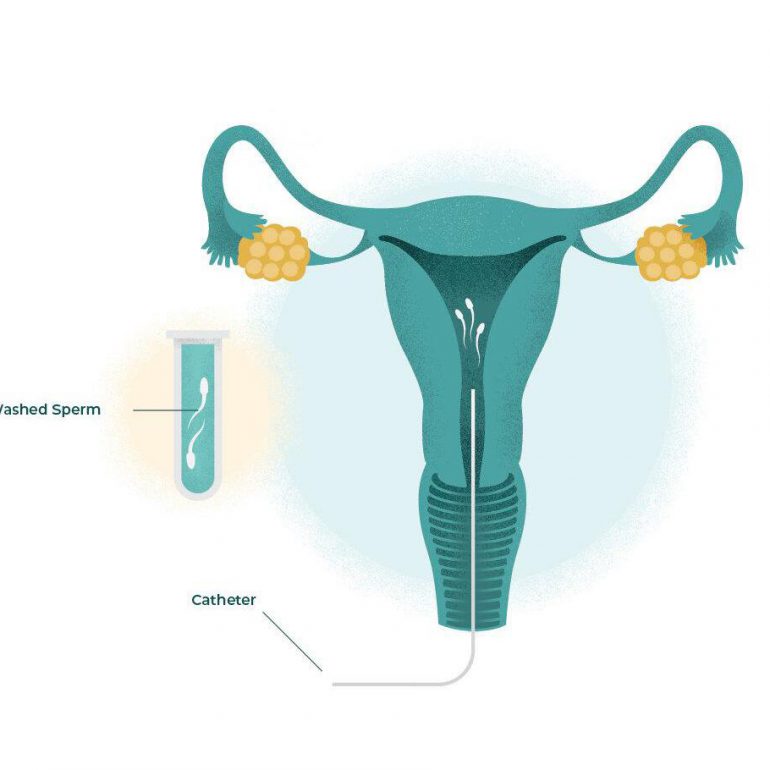
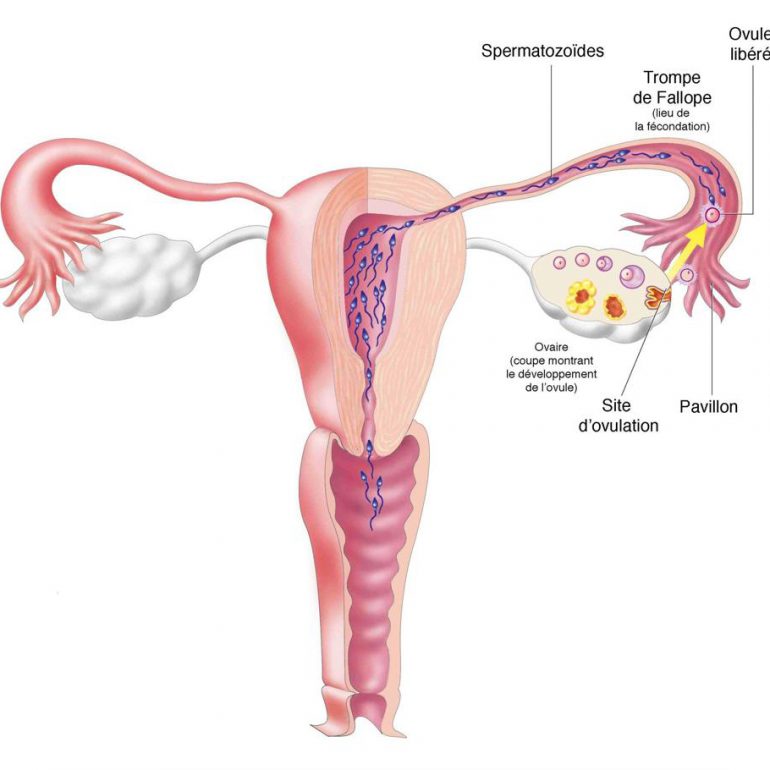
IUI
This may be slightly uncomfortable, a mild period pain sensation but otherwise is relatively quick and painless.
There is no need to take time off work or limit usual daily activities following IUI but you should plan for 2 to 4 visits to the ACU during your treatment cycle for scans and the insemination itself. If you do not have a period 2 weeks after insemination, a pregnancy test should be done. This can be a standard home pregnancy test or you may choose to come to the clinic for a blood test. If the test result is positive we can arrange for you to come in for an early pregnancy scan 3 weeks later (you will be 7 weeks pregnant at this stage).
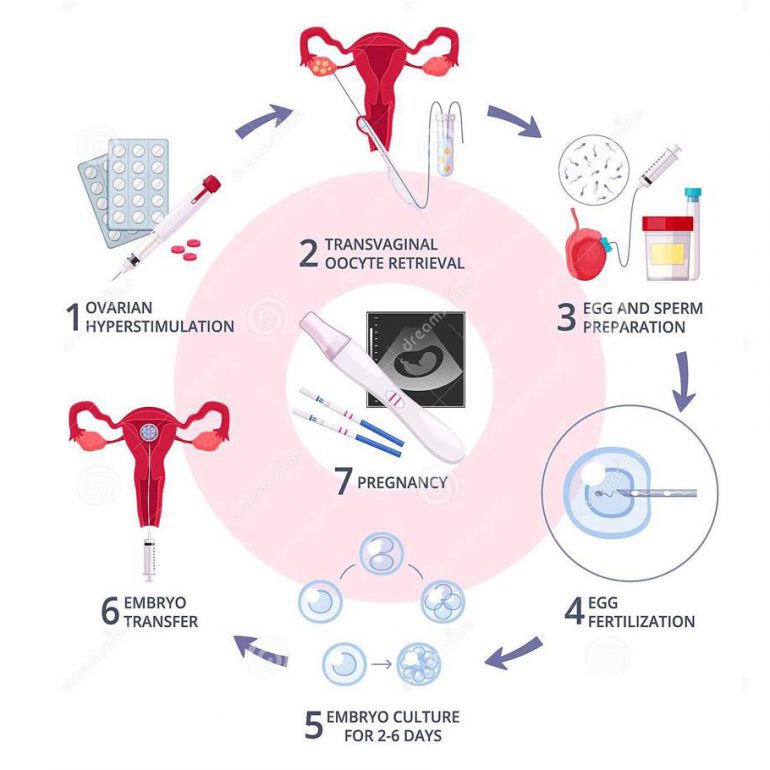
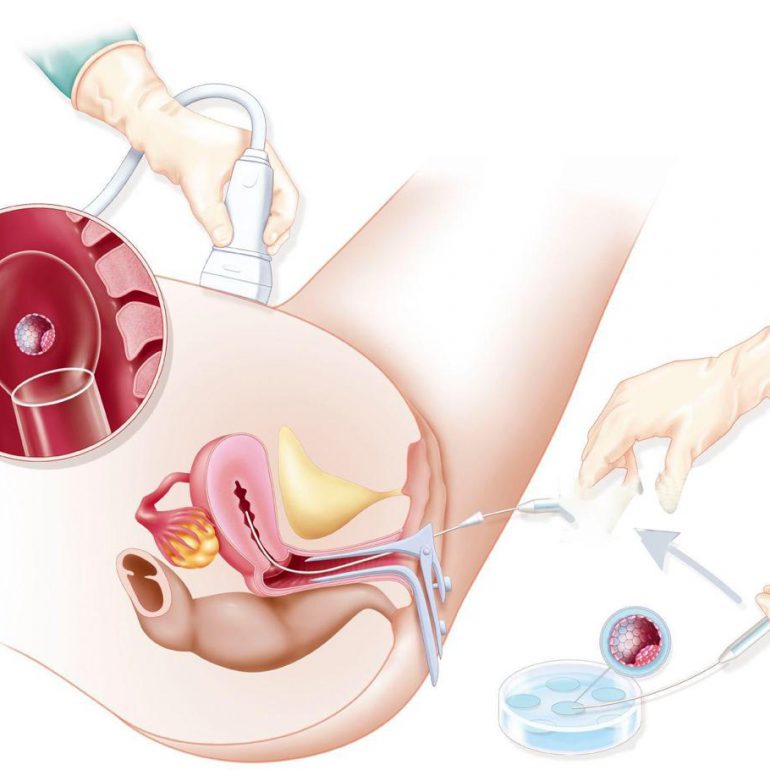
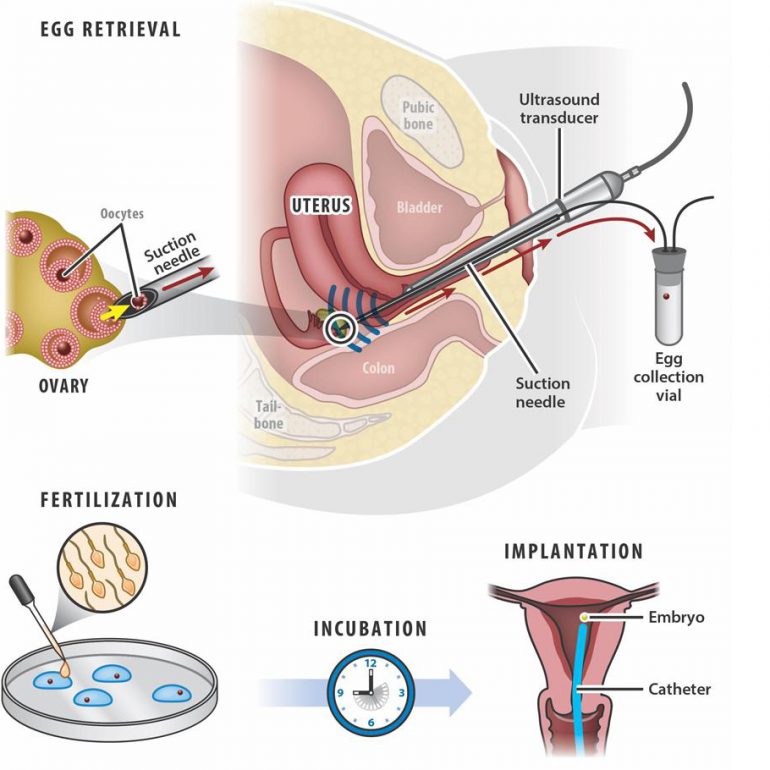
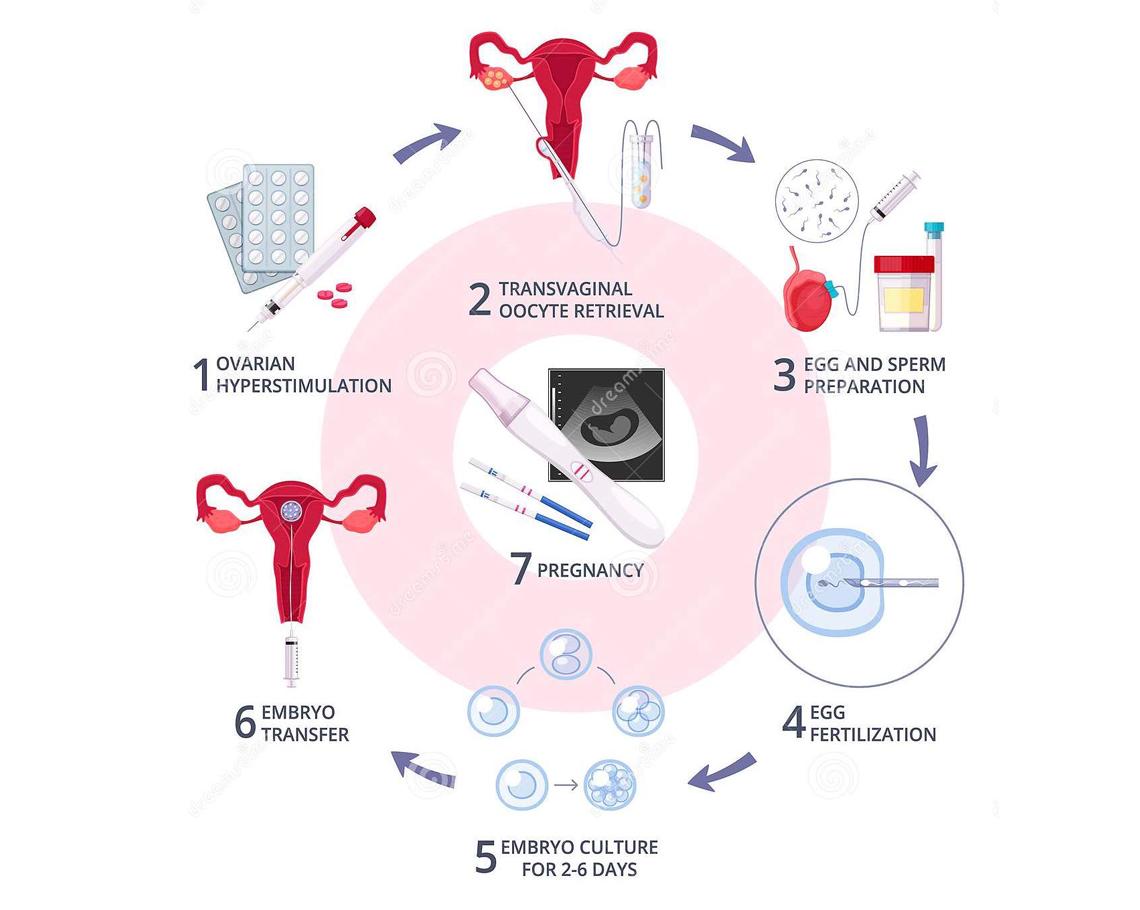
IVF
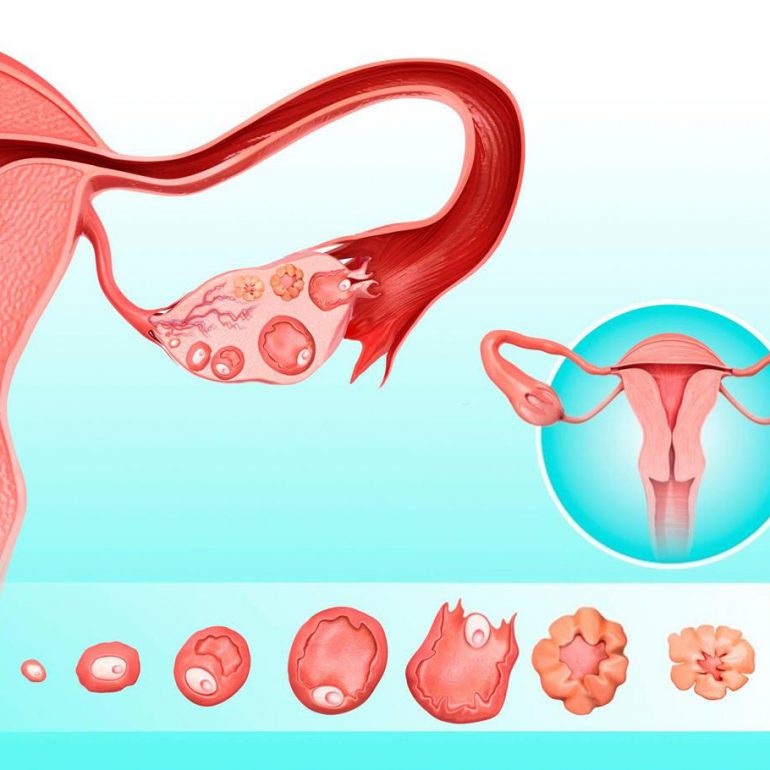
The fertilised eggs are allowed to grow in the laboratory for 2 or 3 days before being replaced in the woman’s uterus (womb). It is the treatment of choice for women with blocked, damaged or absent fallopian tubes but, it is also used when there are moderate sperm abnormalities or the infertility is unexplained. An ovary has a pool of immature eggs.
In a woman’s natural cycle, it is usual to produce one egg each month, which is released from the developing follicle (fluid filled sacs) two weeks before the next period starts. In IVF cycles the aim is to achieve the growth and development of several follicles in order to maximise the chance of collecting several eggs.
- To purse having a biological child with infertility treatment such as: ovulation induction, intrauterine insemination, IVF, ICSI, GIFT and surgery, etc.
- Try to have a child who is biologically related to one partner only e.g. using donated eggs or donor sperm and surrogacy.
- Try to have a child who is biologically not related to either partner through embryo donation.
- Adoption.
ACCEPTING CHILD-FREE LIVING(STAY CHILDLESS)
The decision regarding the management of your infertility is yours and yours alone but it should be noted that the provision of fertility treatments varies greatly from country to country and even in the same country, from clinic to clinic. Before you agree to a fertility treatment, we recommend that you consider the following questions:
- What is the cause of your infertility?
- Why and how the treatment will be given?
- What are the alternatives?
- How much will the treatment cost?
- What are the possible risks and complications?
- How long will you have to undergo treatment in order to give it a reasonable chance to work?
- What is your chance of achieving a pregnancy and a live birth without treatment and how much will the proposed treatment improve your chances of success?